Companies all over the world are moving away from the typical on-premise services they have come to rely on, thanks to the growing popularity of cloud computing and services.
Cloud-based services have changed the way organizations operate, allowing them to access IT infrastructures, platforms, software, and applications through the Internet and other wireless networks.
if you're thinking about transferring your eCommerce business to the cloud then there are three key concepts to understand before moving ahead:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
These platforms have seen considerable growth in the recent ten years, with global revenue rising from roughly $90 billion in 2016 to more than $312 billion in 2020.
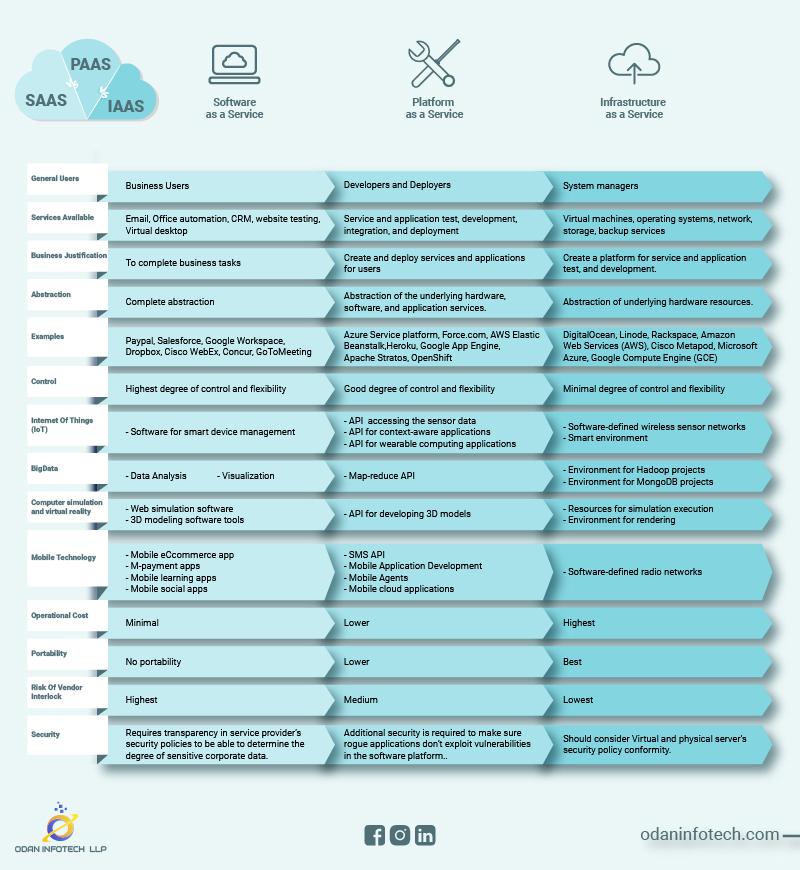
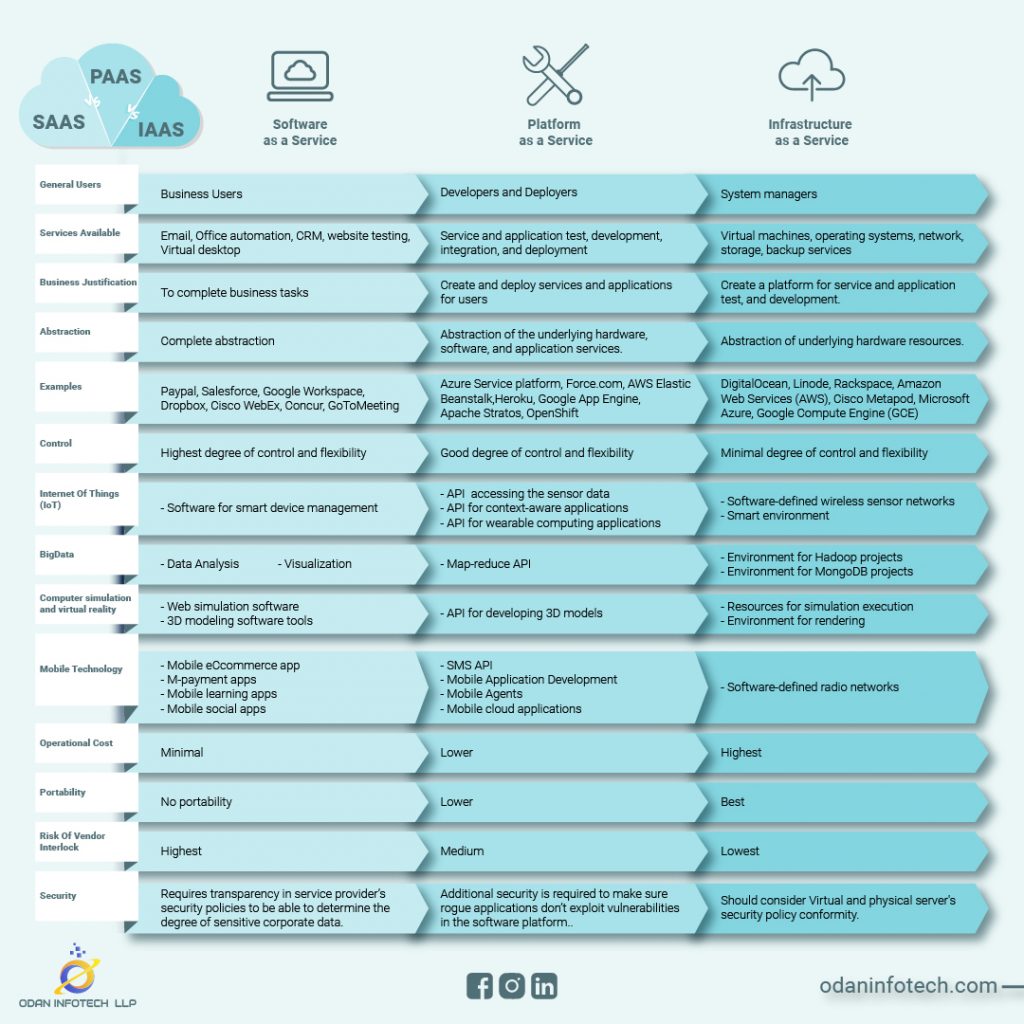
What Is SAAS?
SAAS is an acronym for Service As A Software. Out of all the cloud services, it is the most prevalent one, allowing users to run existing online apps. SaaS provides various software like word processing, email, design software, collaboration software, and other application hosts. One can access these SaaS applications directly through web browsers, eliminating installing any application on a person’s workstation.
A SaaS vendor manages operating systems, servers, data, applications, storage, and many more. Thus, an IT manager only needs to worry about software usage and employee access to it. SaaS works as a model software- deployed in a hosting service that anyone can access via the internet or by using a software delivery model.
Benefits Of Using SaaS
- Easy to access and use
- Scalability
Drawbacks Of Using SaaS
- Lack of integration support
- Transferring sensitive business information to a public-cloud-based SaaS service may result in compromised security and compliance in addition to a significant cost for migrating large data workloads.
- SaaS apps often come in a standardized form, the choice of features may be a compromising tradeoff against security, cost, performance, or other organizational policies.
When To Use SaaS
- Startups and small businesses need to establish an e-commerce site quickly and don't have time to deal with server or software concerns.
- Projects that demand quick, easy, and cost-effective collaboration.
- Tax software, for example, is an example of an application that isn't used very often.
- Web-based and mobile-friendly applications
Organizations Who Uses SaaS
Salesforce, Cisco, WebExDropbox ZenDesk, MailChimp
What Is PAAS?
Platform As A Service, or PAAS, is a cloud delivery service model for a variety of applications. SaaS allows users to scale their apps on an as-needed basis. As a result, developers can create various services and apps directly on the internet. Private, public, or hybrid services are all possible.
Developers and businesses can leverage the foundation provided by PaaS to customize apps quickly and easily. As a result, the developers can concentrate on the application software rather than worrying about numerous infrastructure issues (like software updates, operating systems, etc.). As a result, IT managers are simply responsible for managing the software/application and clearing the clutter.
Benefits Of Using PAAS
- Easy migration to the hybrid model
- Developers may customize apps without having to worry about software maintenance.
- Business policy automation
- Significant reduction in the amount of coding needed
- Simplicity, and convenience
Drawbacks Of Using PaaS
- Lack of scalability
- Vendor lock-in: Because PaaS vendors have unique configuration requirements, organizations may find it difficult to move from one provider to another.
- Data security options may be limited as customers may not be able to deploy services with specific hosting policies.
When To Use PaaS
In a variety of cases, PaaS is advantageous, if not essential. When numerous developers are working on the same development project, PaaS can help streamline procedures. If other vendors are required, PaaS can make the entire process much faster and more flexible. PaaS is very useful if you need to build custom applications.
Organizations Who uses PaaS
OpenShift, Heroku, Force.com, Windows Azure, AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
What Is IAAS?
Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS) is an acronym for Infrastructure As A Service. It is used to provide on-demand services and computer infrastructure. It functions in much the same way as traditional computer hardware (through operating systems, networks, servers, and so on), with the exception that it is virtual. This eliminates the requirement for IT managers to purchase actual gear. They can buy infrastructure as a virtual service from an IaaS provider.
One of the three basic models of cloud service network OS is IaaS. When a customer buys software, a server, cloud storage, network equipment, and other resources, the IaaS provider rents them out as fully outsourced services (as a demand model). IaaS allows for dynamic scaling and resource distribution.
Benefits Of Using IaaS
- The cloud computing model with the most flexibility
- Storage, networking, servers, and processing power can all be deployed quickly and easily.
- The infrastructure is completely under the control of the clients.
- Purchases can be made as needed.
- Easily scalable
Drawbacks Of Using IaaS
- Legacy systems operating in the cloud.
- Internal resources and training. Additional resources and training may be required for the workforce to learn how to effectively manage the infrastructure.
- Security: In an IaaS environment, organizations relinquish control over cloud security to third-party vendors.
When To Use IaaS
- IaaS may be preferred by startups and small businesses to avoid spending time and money on procuring and developing hardware and software.
- Larger firms may choose to maintain complete control over their apps and infrastructure, but they only want to buy what they use.
- Companies with quick expansion appreciate the scalability of IaaS, which allows them to rapidly swap out individual hardware and software as their needs change.
Organizations Who uses IaaS
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine (GCE), IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Rackspace
Conclusion
Each cloud model has its own set of features and functions, and it's critical that your organization must understand the distinctions. There is a cloud solution for you whether you require cloud-based software for storage, a smooth platform for creating customized apps, or complete control over your entire infrastructure without physically managing it.

